Answer:
165.52 g/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
Upon temperature was raised to 100 C part of the initial mass of liquid is gas, exactly: 2.00-0.581 = 1.419 g. This gas occupy a volume of approximately 265 mL, its pressure of 752 mm Hg and its temperature is 100 C. Assuming that this gas behaves as gas ideal we can estimate the molecular weight
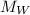 taking into account tha gas ideal law:
taking into account tha gas ideal law:
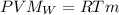 with R= 0.082 atm L/(mol K)
with R= 0.082 atm L/(mol K)
or
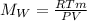
Before using of the formula, we need convert volume units to L (1L=1000 mL) pressure to atm (1 atm=760 mmHg) and temperature to K (K=273+C).
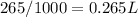
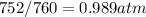
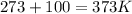
Finally, replacing in the formula
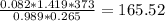 g/mol
g/mol