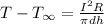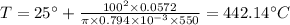Answer:
Steady State Temperature is
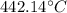
Solution:
As per the question:
Diameter, d = 0.794 mm =
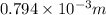
Radius, r =
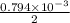
Temperature,
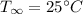 = 298 K
= 298 K
Electrical resistance of the wire, R = 0.0572
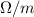
Current, I = 100 A
Surface coefficient, h =
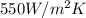
Now,
To calculate the steady-state temperature:
The value of the thermal coefficient of Aluiminium, from the table of physical props of solid, K = 229
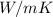
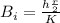
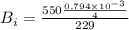
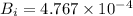
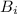 < 0.1
< 0.1
Thus by using lumped capacitance method for the steady steady temperature without radiation: