Answer:
C = 0.875 M
Step-by-step explanation:
- The concentration of the NaOH solution is equal to the number of moles of NaOH divided by the volume:
C = n/V
From the problem we know that V = 15.20 mL = 0.0152 L
So we just need to calculate the moles of NaOH:
- First we calculate the moles of oxalic acid, using its molecular weight:
0.60 g ÷ 90.03 g/mol = 6.66 *10⁻³ mol.
Every 1 mole of oxalic acid is deprotonated by 2 moles of NaOH, so the moles of NaOH are:
6.66 *10⁻³ mol Acid *
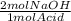 = 0.0133 mol NaOH
= 0.0133 mol NaOH
- The concentration of the NaOH solution is
C = n / V = 0.0133 mol / 0.0152 L = 0.875 M