Answer:
0.86 g
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Pressure = 725 torr
The conversion of P(torr) to P(atm) is shown below:
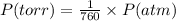
So,
Pressure = 725 / 760 atm = 0.9539 atm
Volume = 225 mL = 0.225 L (1 mL = 0.001 L)
Temperature = 25 °C
The conversion of T( °C) to T(K) is shown below:
T(K) = T( °C) + 273.15
So,
T₁ = (25 + 273.15) K = 298.15 K
Using ideal gas equation as:
PV=nRT
where,
P is the pressure
V is the volume
n is the number of moles
T is the temperature
R is Gas constant having value = 0.0821 L.atm/K.mol
Applying the equation as:
0.9539 atm × 0.255 L = n × 0.0821 L.atm/K.mol × 298.15 K
⇒n = 0.0099 moles
From the reaction,
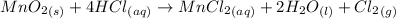
1 mole of chlorine is formed from 1 mole of
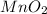
Thus, moles of
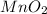 = 0.0099 moles
= 0.0099 moles
Molar mass of
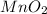 = 86.9368 g/mol
= 86.9368 g/mol
Mass = Moles*Molar mass = 0.0099 moles * 86.9368 g/mol = 0.86 g