Answer:
The sample proportion from Johns Hopkins will have more sampling variability than that from Ohio State.
Explanation:
The number of undergraduates at Johns Hopkins University is approximately 2000.
The number at Ohio State University is approximately 40,000.
For John Hopkins:
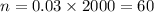
For Ohio state:
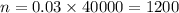
So, the correct answer is :
The sample proportion from Johns Hopkins will have more sampling variability than that from Ohio State.