Answer:
For 1: The correct answer is Option C.
For 2: The correct answer is Option B.
For 3: The correct answer is Option C.
For 4: The correct answer is Option C.
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
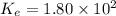
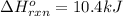
For the given chemical reaction:
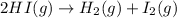
Any change in the equilibrium is studied on the basis of Le-Chatelier's principle. This principle states that if there is any change in the variables of the reaction, the equilibrium will shift in the direction to minimize the effect.
Any change in volume during equilibrium is studied on the basis of change of moles of reactants and products.
When volume is decreased, the equilibrium will shift in the direction which produces fewer moles of gas and when volume is increased, the equilibrium will shift in the direction which produces more moles of gas.
Number of moles of gases on reactant side = [1 + 1] = 2
Number of moles of gases on product side = 2
Change in number of moles = 2 -2 = 0
As, number of moles on both the side of the reaction is same. This means there will be no effect on change in volume.
As, there is no effect of volume on the equilibrium. So, the equilibrium constant remains the same.
Hence, the correct answer is Option C.
 is the constant of a certain reaction at equilibrium while
is the constant of a certain reaction at equilibrium while
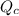 is the quotient of activities of products and reactants at any stage other than equilibrium of a reaction.
is the quotient of activities of products and reactants at any stage other than equilibrium of a reaction.
There are 3 conditions:
- When
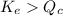 ; the reaction is product favored.
; the reaction is product favored. - When
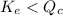 ; the reaction is reactant favored.
; the reaction is reactant favored. - When
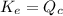 ; the reaction is in equilibrium.
; the reaction is in equilibrium.
As, the value of
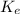 is not changing.
is not changing.
This means that value of
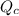 will be equal to
will be equal to
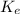
Hence, the correct answer is Option B.
As, the equilibrium constant is not changing. So, the reaction is present at equilibrium.
Hence, the correct answer is Option C.
The reaction is present at equilibrium. So, the concentration of iodine gas will remain the same.
Hence, the correct answer is Option C.