Answer:
10.63 kJ/mol is the
 of the reaction.
of the reaction.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate
 of the reaction, we use Van't Hoff's equation, which is:
of the reaction, we use Van't Hoff's equation, which is:
![\ln ((K_1)/(K_2))=(\Delta H)/(R)[(1)/(T_1)-(1)/(T_2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/a9mt55xiwi5nfgxy5zb0db06xbo46vu9dv.png)
where,
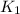 = equilibrium constant at
= equilibrium constant at
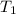
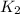 = equilibrium constant at
= equilibrium constant at
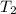
 = Enthalpy change of the reaction
= Enthalpy change of the reaction
R = Gas constant = 8.314 J/mol K
Given :
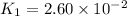
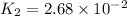
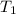 = initial temperature =
= initial temperature =
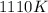
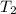 = final temperature =
= final temperature =
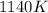
 = ?
= ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![\ln((2.68* 10^(-2))/(2.60* 10^(-2)))=(\Delta H)/(8.314J/mol.K)[(1)/(1110 K)-(1)/(1140 K)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/yw3tdya0020ouzhfisxadlspapsdss7cnt.png)
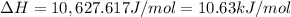
10.63 kJ/mol is the
 of the reaction.
of the reaction.