Answer:
The equilibrium concentration of HCl is 0.01707 M.
Step-by-step explanation:
Equilibrium constant of the reaction =
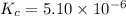
Moles of ammonium chloride = 0.573 mol
Concentration of ammonium chloride =
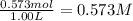
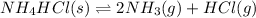
Initial: 0.573 0 0
At eq'm: (0.573-x) x x
We are given:
![[NH_4Cl]_(eq)=(0.573-x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/rdgumdahq8dhih826s2ylbvcf9thme18w9.png)
![[HCl]_(eq)=x](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/e5q900lomi2vsqij5tv9tad3f8n8ddzhpd.png)
![[NH_3]_(eq)=x](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/bmtp4jvs8ywb22lqk1bomyf4q6t6rk37ll.png)
Calculating for 'x'. we get:
The expression of
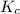 for above reaction follows:
for above reaction follows:
![K_c=([HCl][NH_3])/([NH_4Cl])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/xh39zacemzseqquclrv0u2n69xrszkdyyp.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
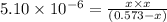
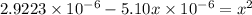
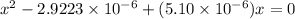
On solving this quadratic equation we get:
x = 0.01707 M
The equilibrium concentration of HCl is 0.01707 M.