Answer:
The equilibrium concentration of
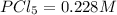 .
.
The equilibrium concentration of
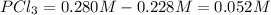 .
.
The equilibrium concentration of
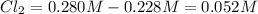 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
Answer:
The equilibrium concentration of HCl is 0.01707 M.
Step-by-step explanation:
Equilibrium constant of the reaction =

Moles of
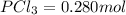
Concentration of
![[PCl_3]=(0.280 mol)/(1.00 L)=0.280 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/1294xum5ke5vg2q17ke35oj6aajilg2bgm.png)
Moles of
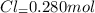
Concentration of
![[Cl_2]=(0.280 mol)/(1.00 L)=0.280M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/sdk6inenn5s4wkl7gyden3kbredg3vyh9f.png)
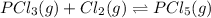
Initial: 0.280 0.280 0
At eq'm: (0.280-x) (0.280-x) x
We are given:
![[PCl_3]_(eq)=(0.280-x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/2e28ispj52mhlt8zgg46lnaakzm0zs8rnu.png)
![[Cl_2]_(eq)=(0.280-x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/qtivy61yppyqcyx5n8aud7ut0awb29l5s7.png)
![[PCl_5]_(eq)=x](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/qss41y7r9n8z7k7cv181n6w8d7gxa9hmsx.png)
Calculating for 'x'. we get:
The expression of
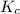 for above reaction follows:
for above reaction follows:
![K_c=([PCl_5])/([PCl_3][Cl_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/8l4jdg6ls22il3qpcc72id4d94uchcinhp.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
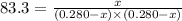
On solving this quadratic equation we get:
x = 0.228, 0.344
0.228 M < 0.280 M< 0.344 M
x = 0.228 M
The equilibrium concentration of
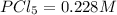 .
.
The equilibrium concentration of
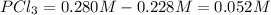 .
.
The equilibrium concentration of
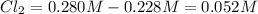 .
.