Answer:
0.1357 M
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) The balanced reaction is shown below as:
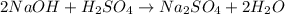
(b) Moles of
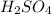 can be calculated as:
can be calculated as:
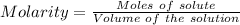
Or,
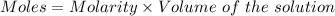
Given :
For
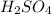 :
:
Molarity = 0.1450 M
Volume = 10.00 mL
The conversion of mL to L is shown below:
1 mL = 10⁻³ L
Thus, volume = 10×10⁻³ L
Thus, moles of
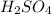 :
:
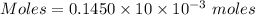
Moles of
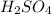 = 0.00145 moles
= 0.00145 moles
From the reaction,
1 mole of
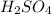 react with 2 moles of NaOH
react with 2 moles of NaOH
0.00145 mole of
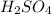 react with 2*0.00145 mole of NaOH
react with 2*0.00145 mole of NaOH
Moles of NaOH = 0.0029 moles
Volume = 21.37 mL = 21.37×10⁻³ L
Molarity = Moles / Volume = 0.0029 / 21.37×10⁻³ M = 0.1357 M