Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Molarity = 0.1 M, Area = 7.2
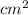
Resistance = 12.553 ohm, Length = 3.6 cm
As it is known that relation between resistance, length and area is as follows.
R =
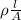
and,
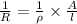
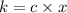
where, k = specific conductivity
c = conductance
x = cell constant
Therefore, value of c =
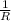 =
=
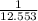 = 0.0796 per ohm
= 0.0796 per ohm
x =
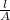 =
=
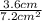
= 0.5 per cm
Hence, calculate the value of specific conductivity as follows.
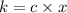
=
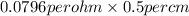
= 0.0398 per ohm per cm
Relation between molar ionic conductivity and specific conductivity is as follows.
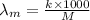
=
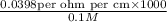
= 398
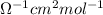
Also,
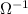 = Siemen
= Siemen
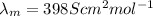
thus, we can conclude that value of molar ionic conductivity of given hydrogen ions is
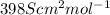 .
.