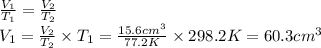Answer:
The volume of helium at 25.0 °C is 60.3 cm³.
Step-by-step explanation:
In order to work with ideal gases we need to consider absolute temperatures (Kelvin). To convert Celsius to Kelvin we use the following expression:
K = °C + 273.15
The initial and final temperatures are:
T₁ = 25.0 + 273.15 = 298.2 K
T₂ = -196.0 + 273.15 = 77.2 K
The volume at 77.2 K is V₂ = 15.6 cm³. To calculate V₁ in isobaric conditions we can use Charle's Law.