Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Potential difference between the ends of a rod, V = 1.1 V
Length of the rod, l = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Area of cross section of the rod,
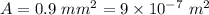
The resistivity of graphite,
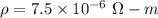
(a) Let R is the resistance of the rod. It is given by :
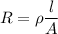
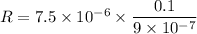
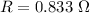
So, the resistance of the rod is 0.833 ohms.
(b) Let I is the current flowing in the wire. It can be calculated using the Ohm's law as :
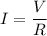
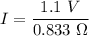
I = 1.32 A
(c) Let E is the electric field inside the rod. The electric field in terms of potential difference is given by :
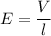
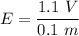
E = 11 V/m
Hence, this is the required solution.