Answer:
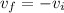
so final velocity is same as initial velocity but its direction is opposite to the direction of initial velocity
Step-by-step explanation:
As we know that when ball throw upwards and again reached to same position then we will have
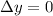
so its displacement is zero
now by kinematics we will have
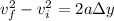
so we have
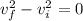
so we have
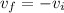
so final velocity is same as initial velocity but its direction is opposite to the direction of initial velocity