Answer:
a) we know that resistance is directly proportional to the length of the conductor as length increases the resistance also increases so to direct the current with least resistance, then the direction is perpendicular to side B only other sides have a larger length than B.
b)
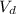 = 4.35 × 10⁻⁴ m/s
= 4.35 × 10⁻⁴ m/s
time = 229.56 s
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
a) we know that resistance is directly proportional to the length of the conductor as length increases the resistance also increases so to direct the current with least resistance, then the direction is perpendicular to side B only other sides have a larger length than B.
Dimension = 0.2m × 0.1m × 0.02m
ρ = 1.69×10⁻⁸ Ωm
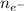 = 8.49 × 10²⁸ e−/m³
= 8.49 × 10²⁸ e−/m³
Potential difference across the solid = 0.001 V
Now,
from Ohm's law V = I × R
here
V is potential difference
I is the current
R is the resistance
or
R =
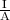
also,
R =
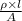
Here, l is the length
A is the area
and,
the drift speed,
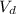 =
=
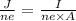
substituting value of I in the above equation, we get
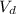 =
=
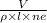
on substituting the values, we get
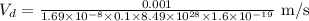
or
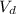 = 4.35 × 10⁻⁴ m/s
= 4.35 × 10⁻⁴ m/s
also,
the time taken, t =
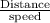
=
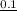
= 229.56 s