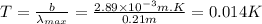Answer:
The temperature associated with this radiation is 0.014K.
Step-by-step explanation:
If we assume that the astronomical object behaves as a black body, the relation between its wavelength and temperature is given by Wien's displacement law.
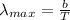
where,
λmax is the wavelength at the peak of emission
b is Wien's displacement constant (2.89×10⁻³ m⋅K)
T is the absolute temperature
For a wavelength of 21 cm,