Step-by-step explanation:
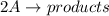
According to mass action,
![\textrm{rate}=-(\Delta[\textrm A])/(2\Delta t)=k[\textrm A]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/oj786zneo067ziqm26kmfe3b60rop1ku4i.png)
Where, k is the rate constant
So,
![(d[A])/(dt)=-k[A]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/guddr1u7xwe13yb8j2c819jb0cnge6tv7o.png)
Integrating and applying limits,
![\int_([A_t])^([A_0])(d[A])/([A]^2)=-\int_(0)^(t)kdt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/lcrg9k4p4joiq5bdlgcfrgalxszvlzhdhr.png)
we get:
![(1)/([A]) = (1)/([A]_0)+kt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/iy3h956c9hxyoel5fkr7rt848li7acr9f9.png)
Where,
![[A_t]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/wbj92t0z4axifcyqa24z3ary269op2iva8.png) is the concentration at time t
is the concentration at time t
![[A_0]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/izynxfnwyud2ghdog9l8ny0mhzwshbud6r.png) is the initial concentration
is the initial concentration
Half life is the time when the concentration reduced to half.
So,
![[A_t]=(1)/(2)* [A_0]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/t4jqi4jdc7ll2oxz95g4qlhaemezos87wo.png)
Applying in the equation as:
![t_(1/2)=(1)/(k[A_o])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/xk4ieyckoa8uncujznu9utfevhemd9bww0.png)