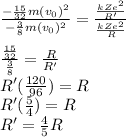Answer:
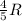
Step-by-step explanation:
Using the law of conservation of energy for both cases, when the proton is at distance R from the nucleus with a final velocity equal to
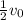 and when the proton is at distance R' from the nucleus with a final velocity equal to
and when the proton is at distance R' from the nucleus with a final velocity equal to
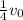 . Recall that initially the two particles are very far apart, so there is no initial potential energy. For the first case, we have:
. Recall that initially the two particles are very far apart, so there is no initial potential energy. For the first case, we have:
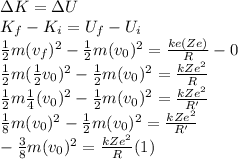
In the same way, for the second case, we have:
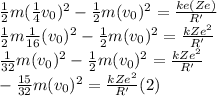
Finally, dividing (2) in (1):