Answer:
A hockey player has an acceleration of -3.1
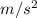 to complete at a speed of 13 m/s it takes him 4.2 seconds.
to complete at a speed of 13 m/s it takes him 4.2 seconds.
Step-by-step explanation:
Applying the 1 \mathrm{st} Equation of Motion
v = u + at
where v = Final Velocity
u = Initial Velocity
a = acceleration
t = time
Given-
v = 0 m/s (Complete stop)
u = +13 m/s
a = -3.1
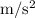 (negative shows deceleration)
(negative shows deceleration)
Putting the Values
0 = 13 + (-3.1)t
or, 3.1t = 13
or, t=
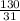
or, t = 4.1935 seconds = 4.2 s