Answer:
Null hypothesis:
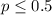
Alternative hypothesis:
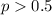
When we conduct a proportion test we need to use the z statistic, and the is given by:
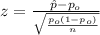 (1)
(1)
For this case we assume that the calculated value its
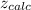
And the p value for this case would be given by:
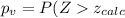
And for this case we want that the
 in order to reject the null hypothesis and on that case we will have enough evidence to conclude that the true proportion of having a girl with the method is >0.5 and that's our interest, so then we need the lowest p value in order to have more evidence to reject the null hypothesisand conclude that the method is effective. The answer for this case would be 0.001.
in order to reject the null hypothesis and on that case we will have enough evidence to conclude that the true proportion of having a girl with the method is >0.5 and that's our interest, so then we need the lowest p value in order to have more evidence to reject the null hypothesisand conclude that the method is effective. The answer for this case would be 0.001.
Step-by-step explanation
Data given and notation
n represent the random sample taken
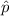 estimated proportion of interest
estimated proportion of interest
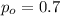 is the value that we want to test
is the value that we want to test
 represent the significance level
represent the significance level
z would represent the statistic (variable of interest)
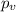 represent the p value (variable of interest)
represent the p value (variable of interest)
Concepts and formulas to use
We need to conduct a hypothesis in order to test the claim that the proportion of having a girl is higher than 0.5, the system of hypothesis on this case are.:
Null hypothesis:
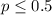
Alternative hypothesis:
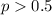
When we conduct a proportion test we need to use the z statistic, and the is given by:
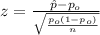 (1)
(1)
For this case we assume that the calculated value its
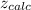
And the p value for this case would be given by:
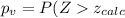
And for this case we want that the
 in order to reject the null hypothesis and on that case we will have enough evidence to conclude that the true proportion of having a girl with the method is >0.5 and that's our interest, so then we need the lowest p value in order to have more evidence to reject the null hypothesisand conclude that the method is effective. The answer for this case would be 0.001.
in order to reject the null hypothesis and on that case we will have enough evidence to conclude that the true proportion of having a girl with the method is >0.5 and that's our interest, so then we need the lowest p value in order to have more evidence to reject the null hypothesisand conclude that the method is effective. The answer for this case would be 0.001.