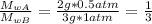Answer:
1/3
Step-by-step explanation:
From the ideal gases law we have:
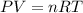
P= pressure, V= volume of the container, n= mol of gas, R=constant of gases and T=temperature.
The molecular weight is:
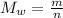
m is mass.
The dalton's law tell us that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressure of every gas.
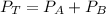
the relationship between the molecular weights is:
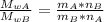 (equation 1)
(equation 1)
where
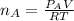
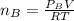
Replacing in equation 1
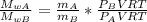
since V and T are constante
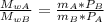
we don't know the partial pressure of B but we know the partial pressure of A since it was the pressure of A at the beginning before adding B (1 atm). We also also know the total pressure of the container with both gases (1.5 atm). From the dalton's law
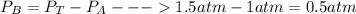
now