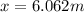Answer: 6.062 m
Step-by-step explanation:
This situation is related to projectile motion or parabolic motion, which has two components: x-component and y-component. Being their main equations as follows:
x-component:
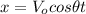 (1)
(1)
Where:
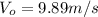 is the jumper's initial velocity
is the jumper's initial velocity
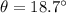 is the angle
is the angle
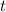 is the time since the jumperleaves the ground and falls again
is the time since the jumperleaves the ground and falls again
y-component:
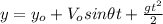 (2)
(2)
Where:
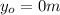 is the initial height of the jumper
is the initial height of the jumper
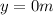 is the final height of the jumper (when it finally hits the ground)
is the final height of the jumper (when it finally hits the ground)
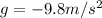 is the acceleration due gravity
is the acceleration due gravity
We need to find the horizontal distance, but firstly we will find the time with (2):
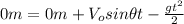 (3)
(3)
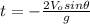 (4)
(4)
Substituting (4) in (1):
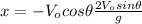 (5)
(5)
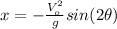 (6)
(6)
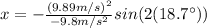 (7)
(7)
Finally: