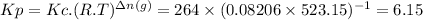Answer:
(a) Kc = 264
(b) Kp = 6.15
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) To calculate Kc we need the molar concentrations of each substance.
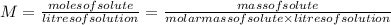
![[PCl_(3)]=(0.220g)/(137.5g/mol * 25.0L ) =6.40 * 10^(-5) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/gc763z0o6ide6bhpm4ljccuvvqvnm0tzy7.png)
![[Cl_(2)]=(2.12g)/(71.0g/mol * 25.0L ) =1.19 * 10^(-3)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/err4z7vvk5wa01db9rslr40nft5pshw798.png)
![[PCl_(5)]=(0.105g)/(208.5g/mol * 25.0L ) =2.01 * 10^(-5) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/a9ae7485fpdrm8suqdhv1laa6gk03n51c7.png)
Then, we replace these concentrations in the Kc expression.
![Kc=([PCl_(5)])/([PCl_(3)]* [Cl_(2)] ) =(2.01 * 10^(-5) )/(6.40 * 10^(-5) * 1.19 * 10^(-3) ) =264](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/piosauyz7y0i72briznhr1655pyg3n1w70.png)
(b) To find out Kp we can use the following expression:
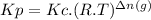
where,
R is the ideal gas constant (0.08206 atm .L /mol . K)
T is the absolute temperature (250°C + 273.15 = 523.15 K)
Δn is gaseous moles of products - gaseous moles of reactants (1 - 2 = -1)
If we replace with the values we have: