Answer:
0.0015moles
0.135g
Step-by-step explanation:
Given parameters:
Volume of NaOH = 25mL = 0.025L
Molarity of NaOH = 0.12M
Unkown:
Number of moles of oxalic acid = ?
mass of oxalic acid = ?
Solution:
The reaction equation is shown below:
H₂C₂O₄ + 2NaOH → Na₂C₂O₄ + 2H₂O
Solving:
We should work from the known to the unknown. The known here is NaOH.
- First find the number of moles of the base, NaOH
- Then using the equation find the number of moles of acid.
- Then find the mass of the acid from the number of moles
##
Number of moles of NaOH = molarity of NaOH x volume = 0.12 x 0.025 = 0.003mole
##
From the equation:
2 moles of NaOH reacted with 1 mole of the acid
0.03 mole of NaOH will react with
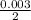 = 0.0015moles of oxalic acid
= 0.0015moles of oxalic acid
##
Mass of oxalic acid = number of moles x molar mass
Molar mass of oxalic acid = (2 x 1) + (2 x 12) + (4 x 16) = 90g/mol
Mass of oxalic acid = 0.0015 x 90 = 0.135g of oxalic acid.