Answer: The mass of carbon tetrachloride required is 293.8 grams.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
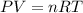
where,
P = pressure of Freon-12 = 1.62 atm
V = Volume of Freon-12 =
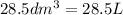 (Conversion factor:
(Conversion factor:
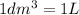 )
)
T = Temperature of Freon-12 =
![21^oC=[21+273]K=294K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/7h54nhyoxlewxbmcja3skd50q1of2tc2dc.png)
R = Gas constant =
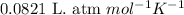
n = number of moles Freon-12 = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
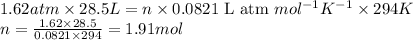
The chemical equation for the formation of Freon-12 follows:
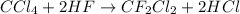
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of Freon-12 is formed by 1 mole of carbon tetrachloride
So, 1.91 moles of Freon-12 will be formed by =
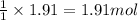 of carbon tetrachloride
of carbon tetrachloride
To calculate the mass of carbon tetrachloride, we use the equation:
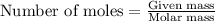
Molar mass of carbon tetrachloride = 153.82 g/mol
Moles of carbon tetrachloride = 1.91 moles
Putting values in above equation, we get:
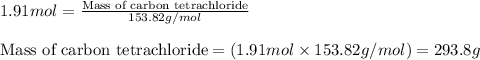
Hence, the mass of carbon tetrachloride required is 293.8 grams.