Answer:
A)The kinetic energy at a point A when a particle of .41 kg moves at a speed of 5.0 m/s is 5.125 J.
B)The speed at point B of the particle of .41 kg with Kinetic Energy 8.5 J is 6.44 m/s.
C)The total Work done by the particle is 3.375 J.
A)Explanation
From the given statements, we know
Mass (m) = 0.41 kg
Velocity = 5.0 m/s
As we know Kinetic Energy (KE) =

Substituting the values in the above equation, we find
Kinetic Energy (KE) =

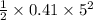 = 5.125 joule
= 5.125 joule
(b) Explanation
From the given statements, we know
Mass (m) = 0.41 kg
Kinetic Energy (KE) = 8.5 J
As we know Kinetic Energy (KE) =

Substituting the values in the above equation, we find
Kinetic Energy (KE) =
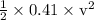 = 8.5 J
= 8.5 J
Or,
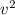 =
=
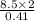 =
=
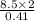
Or, v =
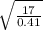 =6.439 m/s ~ 6.44 m/s
=6.439 m/s ~ 6.44 m/s
(c) Explanation
From the above given statements, we know
Kinetic Energy at A = 5.125 J
Kinetic Energy at B = 8.5 J
As we know
Work Done = Change in Kinetic Energy (ΔKE)
So, Work Done (WD) = Kinetic Energy at B - Kinetic Energy at A
WD = (8.5 – 5.125) J = 3.375 J