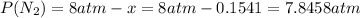Answer:
7.8458 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
For the reaction
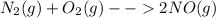
Kp is defined as:
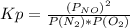
The conditions in the system are:
O2 N2 NO
initial 5 atm 8 atm 0
equilibrium 5-x 8-x 2x
From the stoichiometric relationship in the reaction we know that to produce 2x of NO we need x of N2 and O2.
Replacing the values in the expression for Kp we get
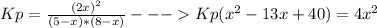
working with this expression
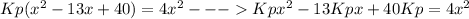

This a quadratic equation with
a=(4-Kp)
b=13*Kp
C=-40*Kp
Replacing the given value for Kp we get:
a=3.9975
b=0.0325
C=-0.1
the solution for this equation is given by the next equation:
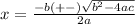
we will get to values for X
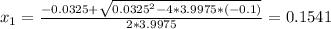
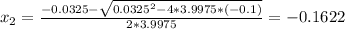
Since negative partial pressures don't have physical meaning the solution for the system is x=0.1541.
So the partial pressure of nitrogen at the equilibrium is