Answer:
13.5PV
Step-by-step explanation:
Through the first process, the change in internal energy is
ΔE=
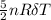
we know that
nRΔT= 2PV-PV= PV
so ΔE= 5/2×PV
work done = PΔV= PV
the heat is Q= 5/2×PV+ PV= 7/2×PV
through the second process, work done is zero
So, Q = ΔE =
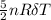
⇒ ΔE= 5/2( 6PV- 2PV) = 10PV
therefore total heat energy transferred to gas = 10PV+ 3.5PV = 13.5PV