Answer:
Option a) The probability of obtaining the sample statistic is 2%, if the null hypothesis is true.
Explanation:
We are given that the p-value is 0.02
Converting it into percentage:
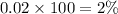
P-value can be explained as:
- P-value can be described as probability of the occurrence of a given event
- The p-value, or probability, is the probability of finding the observed results when the null hypothesis
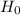 of a study is true.
of a study is true. - If the p-value is less than the chosen significance level then we reject the null hypothesis and accept that the sample gives reasonable evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
- A smaller p-value means that there is stronger evidence in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
- The p-value is the probability to the right of our test statistic.
- The smaller is the p-value, the stronger are the evidence against the null hypothesis and in favor of alternative hypothesis.
Hence, Option a) correctly describes the p-values as:
The probability of obtaining the sample statistic is 2%, if the null hypothesis is true.