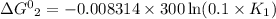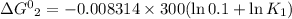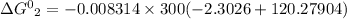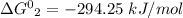Answer:
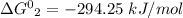
Step-by-step explanation:
The relation between standard Gibbs energy and equilibrium reaction is shown below as:
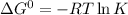
R is Gas constant having value = 0.008314 kJ / K mol
Given temperature, T = 300 K (Source Original)
Given,
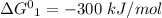
So,
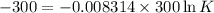
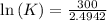
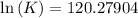
Also,
K₁ = 10*K₂
K₂ = 0.1 K₁
So,