Answer:
Determine the pH of the solution half-way to the end-point on the pH titration curve for acetic acid.
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation for the ionization of acetic acid is
HA + H₂O ⇌ H₃O⁺ + A⁻
For points between the starting and equivalence points, the pH is given by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
![\text{pH} = \text{pK}_{\text{a}} + \log\frac{[\text{A}^(-)]}{\text{[HA]}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/dj1b4x1rj7hlee0jqx9eizxnruentggeot.png)
At the half-way point, half of the HA has been converted to A⁻, so [HA] = [A⁻]. Then,
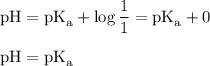
The pKₐ is the pH at the half-way point in the titration.