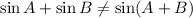Answer:
Langdon is not correct. It means distributive property is not applicable for sines of angles.
Explanation:
According to Langdon
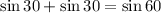
We need to check whether Langdon is correct or not.
Taking LHS,
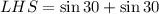
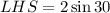
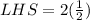
![[\because \sin 30=(1)/(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/high-school/wy2o4du3dg0m67epcszhy6l61oes3grika.png)
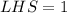
Taking RHS,
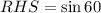
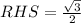
![[\because \sin 60=(√(3))/(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/high-school/urj0i476v3eqd1664d04cp5xfcl2ybteq2.png)
Since LHS ≠ RHS, therefore Langdon is not correct.
It means distributive property is not applicable for sines of angles.