Step-by-step explanation:
Reaction for decomposition of
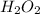 is as follows.
is as follows.
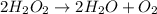
Molarity of
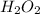 = 2.57 M
= 2.57 M
Volume = 4.20 ml
=
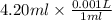
= 0.0042 L
Now, calculate the moles of
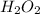 as follows.
as follows.
Moles of
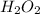 = Molarity × Volume
= Molarity × Volume
=
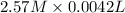
= 0.0107 mol
According to the balanced equation, 2 mole of
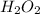 gives 1 mole of
gives 1 mole of
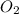 .
.
Hence, 0.0107 mol of
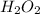 gives 0.00575 mol of
gives 0.00575 mol of
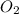 .
.
Partial pressure of
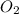 = 0.9624 atm
= 0.9624 atm
Temperature = 300.95 K
Now, using ideal gas equation we will calculate the volume as follows.
PV = nRT
V =
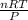
=
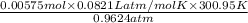
= 0.1475 L
or, = 147.5 ml (as 1 L = 1000 mL)
Thus, we can conclude that volume of
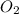 is 147.5 ml.
is 147.5 ml.