Answer:
The point equidistant from the three points (-6,0),(-3,1) and (0,0) is (-3,-3)
Solution:
The given three points are A (-6, 0), B (–3, 1) and C (0, 0)
Let P (x, y) be the point equidistant from these three points.
Distance between two points is given as
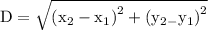
Where
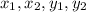 are the x and y co-ordinates
are the x and y co-ordinates
The distance between A (-6, 0) and P(x, y) is:
Using the distance formulae,
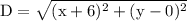
On taking square root we get,
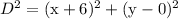 --- eqn 1
--- eqn 1
The distance between B(-3, 1) and P(x, y) is:
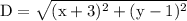
On taking square root we get
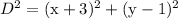 --- eqn 2
--- eqn 2
The distance between C(x, y) and P (0, 0) is:
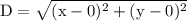
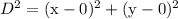 -- eqn 3
-- eqn 3
By equating equation 1 = equation 2 to find the value of y
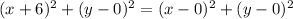
In both the expression
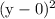 is common so we can cancel it.
is common so we can cancel it.
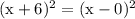
On expanding we get,
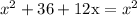
12x = -36
x = -3.
Now find the value of y using equation 3.
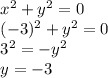
Hence the required points are (-3,-3).