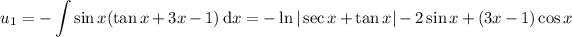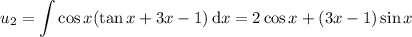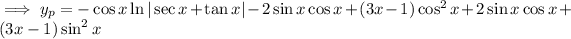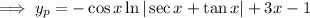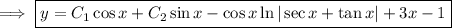The corresponding homogeneous equation
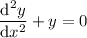
has characteristic equation
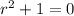
which admits two roots,
 , so the characteristic solution is
, so the characteristic solution is
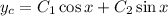
So we know two fundamental solutions,
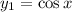 and
and
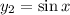 . These two solutions have Wronskian determinant
. These two solutions have Wronskian determinant
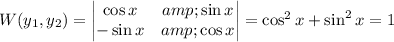
so they are linearly independent.
We use variation of parameters to find a particular solution
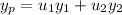 , where
, where