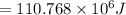Answer:
A) 1384.6 J/g
b)110.768 MJ
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data:
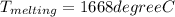
density of titanium = 4.5 g/cm^3
specific heat = 0.544 J/g degree C
heat of fusion = 419 J/g
Pouring temperature for titanium = 1800 degree C
Initial temperature = 25 degree C
a) eneegy for heating unit mass is given as
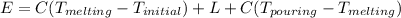
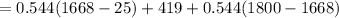
= 1384.6 J/g
b) Total energy to heat 80 kg metal
we know for one unit 1384.6 J/g energy is required
therefore for 80 kg , energy required is
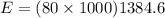
= 110768000 J