Answer:
(a) 0.833 j
(b) 2.497 j
(c) 4.1625 j
(d) 4.995 watt
Step-by-step explanation:
We have given force F = 5 N
Mass of the body m = 15 kg
So acceleration
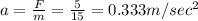
As the body starts from rest so initial velocity u = 0 m/sec
(a) From second equation of motion
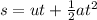
For t = 1 sec
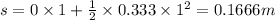
We know that work done W =force × distance = 5×0.1666 =0.833 j
(b) For t = 2 sec
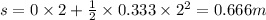
We know that work done W =force × distance = 5×0.666 =3.33 j
So work done in second second = 3.33-0.833 = 2.497 j
(c) For t = 3 sec
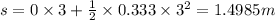
We know that work done W =force × distance = 5×1.4985 =7.4925 j
So work done in third second = 7.4925 - 2.497 -0.833 = 4.1625 j
(d) Velocity at the end of third second v = u+at
So v = 0+0.333×3 = 0.999 m /sec
We know that power P = force × velocity
So power = 5× 0.999 = 4.995 watt