Answer:
The amount of calcium carbonate will increase.
Step-by-step explanation:
K is the constant of a certain reaction when it is in equilibrium, while Q is the quotient of activities of products and reactants at any stage other than equilibrium of a reaction.
- K>Q , reaction will move forward by making more product.
- K<Q , reaction will move backward by making more reactant.
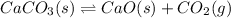
Equilibrium constant of the reaction =
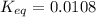
Concentration of
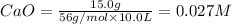
Concentration of
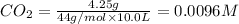
Concentration of
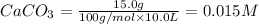
![Q=([CaO][CO_2])/([CaCO_3])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/th5ss7uupd8zh06bzm8xawq8p5vuucv7dm.png)
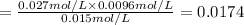
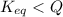
This means that equilibrium will move in backward direction by which amount of calcium carbonate will increase.