Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Temperature =
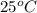 , Total alkalinity =
, Total alkalinity =
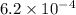 M
M
Alkalinity of phenolphthalein =
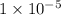 M
M
pH = 7.6, Hardness = 30 mg/L
![[Mg^(2+)] = 1 * 10^(-4)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/2e00fqp9strefr2f7fpvwce4l02qp3rvnh.png) M
M
It is known that total alkalinity is as follows.
Total alkalinity =
![[HCO^(-)_(3)] + [CO^(2-)_(3)] + [OH^(-)] - [H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/98zl6hyfdmstim7fdqcut4qi05rt69aura.png)
Since, pH = 7.6. Hence, concentration of hydrogen ions will be calculated as follows.
pH =
![-log [H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/gopcqwordys161r0cdra5oyonsnub5hpxq.png)
7.6 =
![-log [H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/gopcqwordys161r0cdra5oyonsnub5hpxq.png)
![[H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/axnvi9gez4h3rovfp1qidd16ya8d7gzbon.png) = antilog (-7.6)
= antilog (-7.6)
=
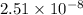 M
M
As, pH + pOH = 14
pOH = 14 - pH
= 14 - 7.6
= 6.4
So,
![[OH^(-)] = 10^(-6.4)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/6g17d8bup5rt4vho1ctye84mpg90l22tcf.png)
=
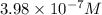
Phenolphthalein alkalinity =
![[CO^(2-)_(3)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/5qn88rj0oirn1s7fqj7w2wk33vj7hlgtwq.png)
![[HCO^(-)_(3)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/9n5pk4q8w82bmimrf5ygjq1fsd9enk8ycz.png) = Total alkalinity - 2[CO^{2-}_{3}] - [OH^{-}] + [H^{+}][/tex]
= Total alkalinity - 2[CO^{2-}_{3}] - [OH^{-}] + [H^{+}][/tex]
=
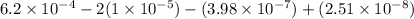
=
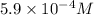
![[Mg^(2+)] = 1 * 10^(-4) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ka3a1hfwhmtdrdcyhqxyu3k1dibsj1w3fv.png) =
=
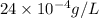
![[Mg^(2+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/cv6hvdw1ngs1847bo8u9v3zixi1zt8zm1k.png) = 2.4 mg/L
= 2.4 mg/L
Ratio of molar mass of
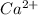 and
and
![[Mg^(2+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/cv6hvdw1ngs1847bo8u9v3zixi1zt8zm1k.png) with
with
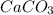 is as follows.
is as follows.
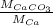 =
=
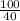 = 25
= 25
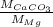 =
=
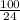 = 4.2
= 4.2
Total hardness =
![2.5[Ca^(2+)] + 4.2 [Mg^(2+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/1vcdc5engxz24wfeqnylx5k8pfmkabrgfj.png)
![[Ca^(2+)] = \frac{\text{total hardness - 4.2(2.4)}}{2.5}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/p4q4xwxx1qfj9xqr8q5dx51qujt3tc7g9j.png)
=
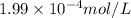
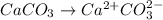
![[Ca^(2+)][CO^(2-)_(3)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/txr5eso304o9hj28264wjpl1623js8xe8y.png) =
=
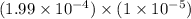
=
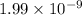
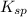 of
of
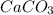 =
=
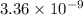
Since,
![[Ca^(2+)][CO^(2-)_(3)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/txr5eso304o9hj28264wjpl1623js8xe8y.png) >
>
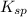
Hence, the water is slightly unsaturated with
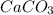 .
.