Answer:
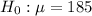 and
and
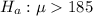
Explanation:
The null hypothesis
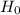 states that a population parameter (such as the mean, the standard deviation, and so on) is equal to a hypothesized value. We can write the null hypothesis in the form
states that a population parameter (such as the mean, the standard deviation, and so on) is equal to a hypothesized value. We can write the null hypothesis in the form
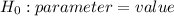
In this context, the investigator's null hypothesis should be that the average total weight is no different than the reported value by the FAA. We can write it in this form
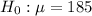 .
.
The alternative hypothesis
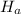 states that a population parameter is smaller, greater, or different than the hypothesized value in the null hypothesis. We can write the alternative hypothesis in one of three forms
states that a population parameter is smaller, greater, or different than the hypothesized value in the null hypothesis. We can write the alternative hypothesis in one of three forms
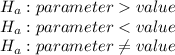
The investigator wants to know if the average weight of passengers flying on small planes exceeds the FAA guideline of the average total weight of 185 pounds. He should use
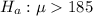 as his alternative hypothesis.
as his alternative hypothesis.