Answer:
The final temperature of the solution in the calorimeter is 28,7°C
Step-by-step explanation:
A -ΔH means that when you dissolve CaCl₂ you will produce heat. This heat you produce is:
3,3g CaCl₂×
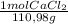 ×82800J/mol = 2462,1 J
×82800J/mol = 2462,1 J
The specific heat capacity of solution is:
q = c×m×ΔT
Where q is energy: (2462,1J)
c is heat capacity of the solution (4,18J/g°C)
m is mass of solution (103,3g)
And ΔT is (T-23°C)
Solving for T:
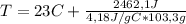
T = 28,7°C
I hope it helps!