Step-by-step explanation:
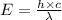
where,
E = energy of photon = ?
h = Planck's constant =
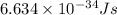
c = speed of light =
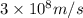
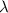 = Wavelength of the radiation
= Wavelength of the radiation
As we can see that wavelength and energy of the radiation are inversely related to each other.So with increase in energy wavelength decreases and vice versa.
Given: The energy of different of different energy levels in an hypothetical model of atom;
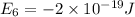
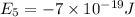
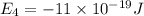
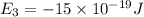
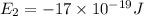
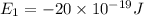
a)If the electron is initially in the n = 4 level. Then maximum difference of energy in energy levels will corresponds to shortest wavelength.
So,
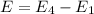
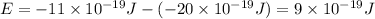
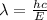
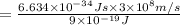
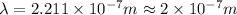
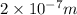 is the shortest wavelength of radiation that could be emitted.
is the shortest wavelength of radiation that could be emitted.
b) Ionization energy of the atom in its first excited state.
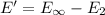
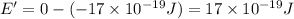
Ionization energy of the 1 mole :
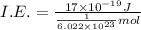
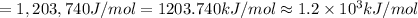
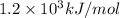 is the ionization energy of the atom in its first excited state.
is the ionization energy of the atom in its first excited state.