Answer:
v = 301.62 km/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
The work function of the magnesium = 3.68 eV
Energy in eV can be converted to energy in J as:
1 eV = 1.6022 × 10⁻¹⁹ J
So, work function =
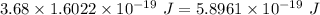
Using the equation for photoelectric effect as:
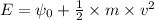
Also,
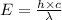
Applying the equation as:
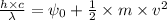
Where,
h is Plank's constant having value
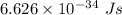
c is the speed of light having value
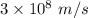
m is the mass of electron having value
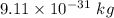
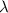 is the wavelength of the light being bombarded
is the wavelength of the light being bombarded
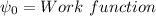
v is the velocity of electron
Given,
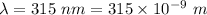
Thus, applying values as:
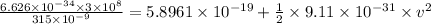
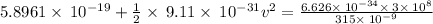
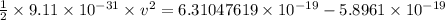
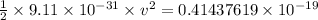
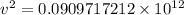
v = 3.0162 × 10⁵ m/s
Also, 1 m = 0.001 km
So, v = 301.62 km/s