Answer:
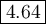
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation for the buffer is
HC₇H₅O₂ + H₂O ⇌ H₃O⁺ + C₇H₅O₂⁻; Kₐ =6.3 × 10⁻⁵
Let's rewrite it as
HA + H₂O ⇌ H₃O⁺ + A⁻
1. Moles of sodium benzoate
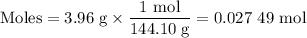
2. Concentration of benzoate ion
![[\text{A}^(-)] = \frac{\text{0.027 49 mol}}{\text{1 L}} = \text{0.027 49 mol/L }](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/eakihv89cmz22y1agu5eb827xgvlw5dtqs.png)
3. Calculate pKₐ
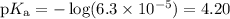
4. Calculate the pH
We can use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to get the pH.
![\begin{array}{rcl}\text{pH} & = & \text{pK}_{\text{a}} + \log\frac{[\text{A}^(-)]}{\text{[HA]}}\\\\& = & 4.20 +\log(0.02749)/(0.0100)\\\\& = & 4.20 + \log2.749 \\& = & 4.20 + 0.4390\\& = & 4.64\\\end{array}\\\text{The pH of the buffer is $\large \boxed{\mathbf{4.64}}$}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ozuu2u4b1iba20pkljy1o69426pnxq8apq.png)