Answer:
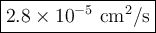
Step-by-step explanation:
The Wilke-Chang equation for the liquid diffusion coefficient is
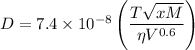
where
D = diffusion coefficient in square centimetres per second
T = kelvin temperature
x = an association parameter for the solvent
M = molar mass of solvent
η = viscosity of solvent in centipoises
V = molar volume of solvent at normal boiling point in cubic centimetres per mole
Data:
T = 289 K
x = 2.6
M = 18.02 g/mol
η = 0.890 cP
V = 18.9 cm³/mol
Calculation:
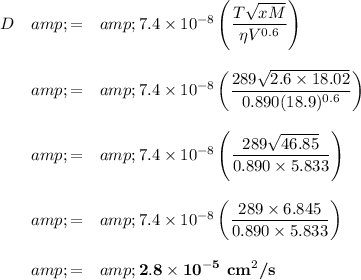
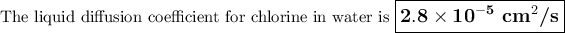
The published value is 1.25 × 10⁻⁵ cm²/s.