Answer:
a) 336.6 MPa
b) 345.87 MPa
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Pressure at the top of a vertical oil well = 140 bars =14 MPa
Depth of the oil well = 6000 m
Depth of the natural gas = 4700 m
Density of oil, ρ = 700 kg/m³
Temperature at the bottom of the well, T = 15° C = 15 + 273 = 288 K
Compressibility factor for natural gas, Z=0.80
molecular weight of natural gas = 18.9
Now,
Z=

P is the pressure 14 MPa = 14000000 Pa
V is the volume
T is the temperature
R is the ideal gas constant = 8.314 J / (mol·K)
on substituting the respective values, we get
0.80 =
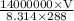
or
V = 1.36 × 10⁻⁴ m³
Now,
Assuming for 1 kg of natural gas
Density of natural gas will be equal to reciprocal of the volume obtained i.e
Density of gas =
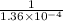
or
Density of gas, ρₐ = 7308.62 Kg/m3
Therefore,
a) Pressure at natural gas-oil interface
P₁ = ρₐ × g × h
at the interface, h = 4700 m.
therefore,
Pressure at natural gas-oil interface, P₁ = 7308.62 × 9.81 × 4700
= 336949956 Pa
= 336.6 MPa
b) Pressure at the bottom of the well, P = P₁ + ( ρₐ × g × (6000 - 4700) )
or
P = 336949956 + ( 700 × 9.81 × (6000 - 4700) )
or
P = 345877056 Pa
or
P = 345.87 MPa