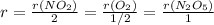Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Let us consider the reaction:
2 NO₂ + 1/2 O₂ ⇄ N₂O₅
The rate of formation of a substance is equal to the change in concentration of the product divided the change in time:
![r(N_(2)O_(5))=(\Delta [N_(2)O_(5)] )/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/7cgygepsy7fppkgr2s0kyhqcmicyt3vyys.png)
The rate of disappearance of a reactant is equal to to the change in concentration of the reactant divided the change in time, with a negative sign so that the rate is always a positive variable.
![r(NO_(2))=-(\Delta[NO_(2)] )/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/i1hiu23xxvdhqkdzdy64971iodx9qu5pl6.png)
![r(O_(2))=-(\Delta[O_(2)] )/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/1ocxte11nhl4x19ocecipwzld8qxahaio9.png)
The rate of the reaction is equal to the rate of any substance divided its stoichiometric coefficient. In this way, we can relate these expressions: