Answer:
K still the same value
Explanation:
given a reaction aA+bB<->cC+dD the constant K is defined as:
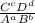
K is a constant so it won't change the value. Instead, the values of C and D are going to change. The position of equilibrium moves because of the need to keep a constant value for the equilibrium constant.