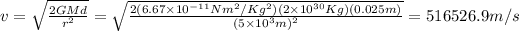Answer:
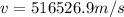
Step-by-step explanation:
The force to which the object of mass m is attracted to a star of mass M while being at a distance r is:
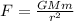
Where
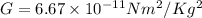 is the gravitational constant.
is the gravitational constant.
Also, Newton's 2nd Law tells us that this object subject by that force will experiment an acceleration given by F=ma.
We have then:
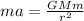
Which means:
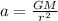
The object departs from rest (
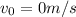 ) and travels a distance d, under an acceleration a, we can calculate its final velocity with the formula
) and travels a distance d, under an acceleration a, we can calculate its final velocity with the formula
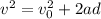 , which for our case will be:
, which for our case will be:
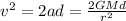
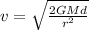
We assume a constant on the vecinity of the surface because d=0.025m is nothing compared with
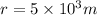 . With our values then we have:
. With our values then we have: