Answer:
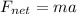
Step-by-step explanation:
Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force exerted on it, according to the formula:
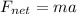
where
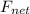 is the net force on the object
is the net force on the object
m is its mass
a is its acceleration
The other statements are wrong because they represent other laws of physics, namely:
When an object puts a force on another object, the second object puts a force back on the first, equal in magnitude but opposite in direction --> Newton's third law
The total energy through any process is conserved --> law of conservation of energy
Objects tend to keep their motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced outside force --> Newton's first law